Semantics is the study of the meanings of words and phrases in a language.
Semantic elements = elements with a meaning.
A semantic element clearly describes its meaning to both the browser and the developer.
Examples of non-semantic elements: <div> and <span> - Tells nothing about its content.
Examples of semantic elements: <form>, <table>, and <article> - Clearly defines its content.
 |
Yes |
 |
Yes |
 |
Yes |
 |
Yes |
 |
Yes |
HTML5 semantic elements are supported in all modern browsers.
Many web sites contain HTML code like:
<div id="nav"> <div class="header"> <div id="footer">
to indicate navigation, header, and footer.
HTML5 offers new semantic elements to define different parts of a web page:
|
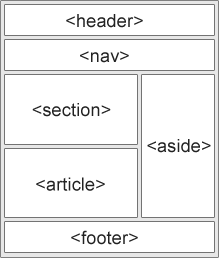 |